Reviewed by Dr. Devashish Raturi (PT)
Specialist in Physical Medicine & Rehabilitation with expertise in chronic pain, joint disorders, and postural dysfunctions. Delivers evidence-based musculoskeletal rehabilitation focused on functional movement, pain relief, and posture correction. Skilled in clinical movement assessment, orthotic prescription, and structured exercise therapy for long-term functional recovery.
January 5, 2026
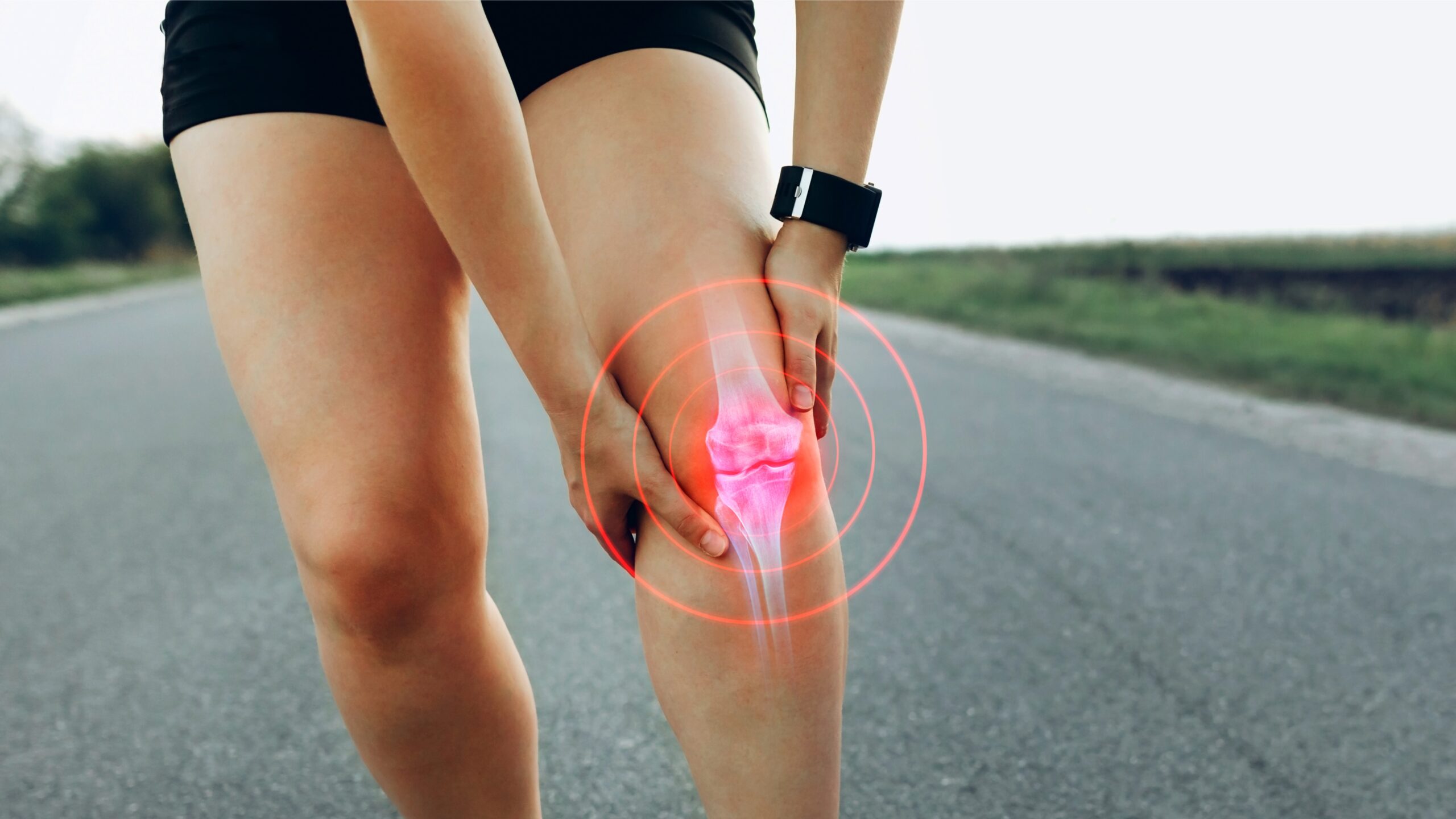
What is ACL injury?
Low back pain (LBP) is one of the most common health problems worldwide. It can range from a dull ache to sharp, debilitating pain that interferes with daily activities like sitting, walking, or bending. LBP affects people of all ages and is a leading cause of disability and missed workdays. While it is often caused by strain or overuse, underlying conditions like herniated discs or arthritis can also contribute.
How does it happen?
The ACL plays a vital role in stabilizing the knee by preventing excessive forward movement of the tibia relative to the femur and controlling rotational forces. When the ACL is injured, it disrupts this stabilization, leading to a compromised ability to control movements. This instability can result from both physical damage to the ligament and neurological deficits affecting proprioception—the body’s ability to sense its position in space. Without proper balance and proprioceptive training, individuals may struggle with dynamic movements, increasing their risk of further injury.
What is the role of balance training?
Balance training can be integrated into various phases of ACL rehabilitation and includes several effective strategies:
1. Static Balance Exercises: Standing on one leg or using balance boards to improve stability.
2. Dynamic Balance Exercises: Incorporating movements like single-leg squats or reaching exercises while balancing.
3. Proprioceptive Training: Using unstable surfaces such as wobble boards or Bosu balls to challenge balance.
4. Agility Drills: Performing lateral shuffles or cone drills to enhance dynamic stability.
5. Functional Movement Patterns: Practicing sport-specific movements that require balance and coordination.
How does it work?
– Static Balance Exercises: These exercises help strengthen stabilizing muscles around the knee and improve overall balance by challenging the bodys ability to maintain equilibrium on a single leg. This foundational strength is critical for preventing falls and maintaining stability during activities.
– Dynamic Balance Exercises: Engaging in movements like single-leg squats enhances coordination and strengthens muscles involved in stabilizing the knee during dynamic activities. This prepares the body for real-life movements that involve changes in direction.
– Proprioceptive Training: Training on unstable surfaces enhances proprioception by forcing the body to adapt to changing conditions. This improves the nervous systems ability to activate muscles around the knee joint, enhancing stability and reducing the risk of re-injury.
– Agility Drills: These drills mimic sports-related movements, improving reaction time and dynamic control. By practising agility, individuals can better prepare for the demands of their sport while reinforcing proper movement patterns that protect the knee.
– Functional Movement Patterns: Practicing specific movements related to an athletes sport helps ensure that they can perform these actions safely. This type of training builds confidence and prepares individuals for a successful return to their sport.
Want to know more about ACL?
For further reading on ACL rehabilitation, consider exploring these articles:
Incorporating balance training into ACL rehabilitation is essential for restoring function and preventing future injuries. By focusing on stability and proprioception, individuals can enhance their recovery process and safely return to their favourite activities. Always consult with a healthcare provider or physical therapist before starting any new rehabilitation program to ensure it aligns with your specific needs.