Reviewed by Dr. Karan Raj Jaggi
Dr. Karan Raj Jaggi is a triple board-certified, internationally trained orthopaedic surgeon super-specialising in regenerative orthopaedics, sports injuries and fast-track joint replacements.He currently serves as the Chief Medical Officer and Head, Regenerative Orthopaedics at OSSO Orthopaedic Centres, where he leads cutting-edge orthopaedic care with a focus on holistic, patient-centric treatments.
December 15, 2025
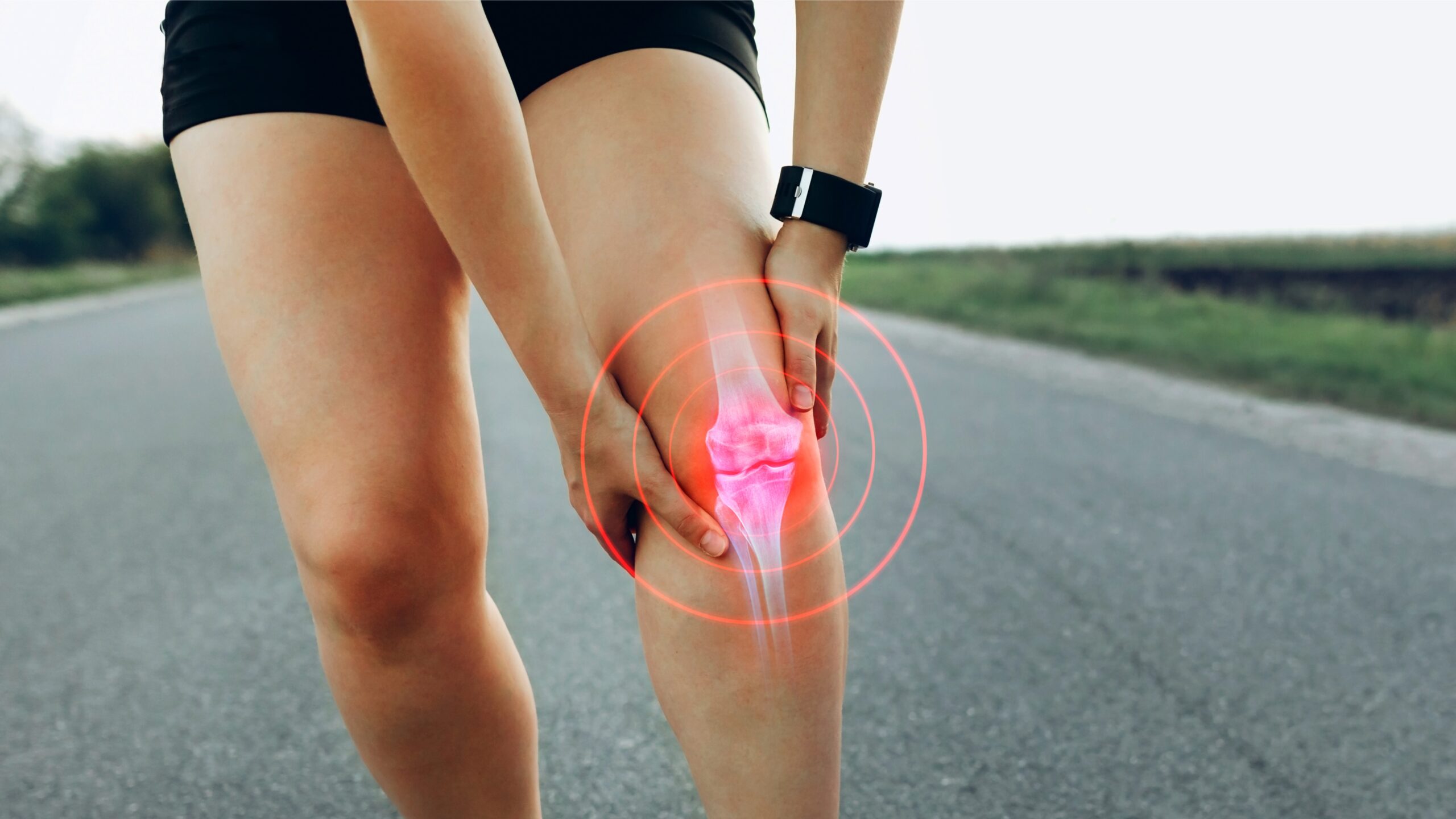
Knee pain is one of the most common musculoskeletal complaints, and while many cases improve with rest, physical therapy, or medication, there are times when knee surgery becomes a necessary option. Knowing when to seek a doctor’s evaluation for possible knee surgery can help prevent long-term damage and restore a better quality of life.
1. Persistent Pain That Doesn’t Improve
If you’ve been dealing with knee pain for several weeks or months despite conservative treatments it’s time to consult a doctor. Non-surgical treatments usually include:
Rest and activity modification
Physical therapy
Ice or heat therapy
Anti-inflammatory medications
Corticosteroid or hyaluronic acid injections
If these methods fail to bring meaningful relief, a surgical consultation may be appropriate.
2. Difficulty Performing Daily Activities
You should see a doctor if knee pain is affecting your ability to:
Walk short distances
Climb stairs
Sit down or stand up easily
Perform work-related tasks
Enjoy sports or recreational activities
When everyday movement becomes difficult or painful, it may signal structural damage that requires a specialist’s evaluation.
3. Knee Instability or “Giving Way”
A knee that feels unstable can indicate ligament injuries such as an ACL tear, PCL tear, or severe meniscus damage. These injuries often require surgical repair especially in active individuals, athletes, or those with physically demanding jobs.
Seek medical attention if you notice:
Sudden buckling
A feeling that the knee won’t support your weight
Repeated episodes of instability
4. Severe Swelling, Stiffness, or Limited Range of Motion
Frequent or persistent swelling is a sign of inflammation or internal injury. Extreme stiffness or being unable to fully bend or straighten your knee may indicate:
Meniscus tears
Loose bone fragments
Advanced arthritis
Scar tissue buildup
A doctor can use imaging tests such as an MRI or X-ray to determine if surgery is needed.
5. Knee Deformity
Visible knee deformities such as bowing, shifting to one side, or misalignment should be evaluated promptly. Structural deformities may worsen over time and can accelerate joint damage, increasing the need for corrective surgery.
6. Failure of Previous Treatments
If you’ve tried multiple non-surgical treatments over a significant period and symptoms keep returning, it may be a sign that the underlying issue requires surgical correction. This is common in cases like:
Chronic meniscus tears
Recurrent patellar dislocations
Advanced osteoarthritis
7. After a Traumatic Injury
Seek immediate medical attention if you experience:
A popping sound followed by pain
Inability to bear weight
Rapid swelling within a few hours
Severe pain after a fall or accident
These can be signs of fractures, torn ligaments, or cartilage injuries that may require surgical intervention.
8. Pain That Interferes With Sleep
If knee pain is keeping you awake at night or preventing comfortable sleeping positions, it may indicate that the condition is progressing. Chronic nighttime pain is common in advanced arthritis and may suggest the need for knee replacement discussions.
9. Loss of Mobility or Declining Quality of Life
When knee problems prevent you from enjoying hobbies, work, or daily activities you once participated in without difficulty, it’s an important sign to seek medical evaluation. Surgery is often recommended when it significantly improves long-term mobility and life quality.
When Surgery Becomes the Right Option
A doctor may recommend knee surgery if:
Imaging tests confirm structural damage
Non-surgical treatments have failed
Pain significantly reduces mobility or independence
Your condition is progressing and causing long-term harm
Types of knee surgery can include arthroscopy, ACL reconstruction, meniscus repair, osteotomy, or total knee replacement depending on the diagnosis.
Deciding when to see a doctor for knee surgery is not always straightforward, but persistent pain, instability, difficulty performing everyday tasks, and loss of mobility are all strong indicators. Early evaluation by an orthopedic specialist can help identify the problem, recommend appropriate treatments, and prevent further joint damage.
If knee pain is affecting your life, don’t wait consult a healthcare professional to explore the best path forward.